Which Best Describes Seismic Tectonic Creep
Fault Creep _____ is a measurement of displacement on the fault surface. A seismograph B seismogram C seismology D vulcanology E tectonics 5.

Igure 7 6 Earthquakes Generate Pressure P Or Primary And Shear S Or Secondary Waves That Can Be D Earth And Space Science Earth Science Geography Lessons
Earth Sciences questions and answers.

. 19 Which of the following best describes a seismic gap. Which tectonic boundary is associated with regional metamorphism. Convergent subduction-zone boundary b.
In practice driven by the geodetic data one would have to use an appropriate model to describe the tectonic creep process eg as by Hetland et al. When creep is only allowed on the part of the fault with no coseismic slip z lock 15 there is an even greater disparity in post-seismic creep compared to the model in which we allow post-seismic creep in all non-asperity regions. The scientific study of earthquakes and seismic waves is known as _____.
TIME DEPENDENCE OF POSTSEISMIC CREEP 2of18 B10404. Shaking particle motion at right angles to the direction of wave travel. Unusually quiet zones along typically active faults.
Which tectonic boundary is responsible for the most powerful and destructive earthquakes recorded. Surface wave-a seismic wave that travels along the ground surface. What best describes the movement of P waves.
A Dip-Slip B Transform C Convergent. A Himalayas B Java C Hawaii D Aleutian Islands E Iceland 4. Cause structural damage Tectonic creep - the slow continuous movement of rock or sediment along a fracture Also called tectonic creep.
Which of the following best describes a seismic gap. This surface wave moves up and down. These rheologies are presented below and then included in a simple model of postseismic deformation.
A short summary of this paper. Seismic anisotropy and mantle creep in young orogens. Fault Creep D Megathrusting.
Geology Exam 2 Chapter 11. Due to the strong dependence of the predicted creep on assumptions of where post-seismic creep is. Which of the following is a characteristic of an S wave.
Have the slowest velocity. Earthquakes occur on faults - strike-slip earthquakes occur on strike-slip faults normal earthquakes occur on normal faults and thrust earthquakes occur on reverse or thrust faults. Equation best describes this process.
η is two orders of magnitude higher for a creep rate of 1017 s1 instead 1014 s1. Amongst all seismic waves surface waves __________. Governments support the worldwide seismic network because it can detect nuclear bomb tests.
Fault creep Choose one. The fault surface can be vertical horizontal or at some angle to the. When an earthquake occurs on one of these faults the rock on one side of the fault slips with respect to the other.
A Unusually quiet zones along typically active faults 20 ________ measures the total energy released during an earthquake by determining the average amount of slip on the fault the area of the fault surface that slipped and the strength of the faulted rock. Which of the following best describes a seismic gap. Much later the study of solid state creep suggested that mantle material deforms and has a viscosity which allows movement of rigid plates at its surface.
Geophysical Journal International 2002. Full PDF Package Download Full PDF Package. Most of our knowledge about Earths interior comes from _.
Hot spot that is not on a plate boundary c. Which of the following locations is the best example of continental crust colliding with continental crust. Also applied to slow movement of landslide masses down a slope because of gravitational forces.
Surface waves are generally strongest close to the epicenter. Which of the following best describes a seismic gap. Which statement best describes the tectonic setting of the central and southern California coast today.
Which tectonic boundary is associated with megathrust faults. Fault creep is an older term that has been most often used for slip in the shallow. 37 Full PDFs related to this paper.
Since the theory of plate tectonics was first introduced. Fault creep _____ are instruments that sense earthquake waves and transmit them to a recording device. Always mark places where plates are converging never where theyre diverging.
10 We consider three candidate rheologies to describe the behavior of rocks in the postseismic time interval velocity-strengthening friction Newtonian viscosity and ductile creep. A A down-dropped valley bound by normal faults. Slow more or less continuous movement occurring on faults due to ongoing tectonic deformation.
Tectonic creep is the almost constant movement of certain faultblocks that allows strain energy to be released without causingmajor earthquakes. Convergent collision-zone boundary Based on. Are usually toward the centers of tectonic plates.
The elastic rebound associated with earthquakes is an example of ________ deformation. 2010-01-18 1436. Faults that undergo significant and or ongoing creep are likely to be aseismic or capable of only small or moderate earthquakes.
View Test 3docx from EAR 312 at California State University Dominguez Hills. Please note that the assumption of a slower creep rate results in higher viscosity values eg. Unusually quiet zones along typically active faults The ________ is a newer scale that measures the total energy released during an earthquake by determining the average amount of slip on the fault the area of the fault surface that slipped and the strength of the faulted rock.
Active Tectonics At Uc Berkeley

Desert Landforms 1 Types Of Deserts Wind School Landforms Geography Revision Geography For Kids Physical Geography
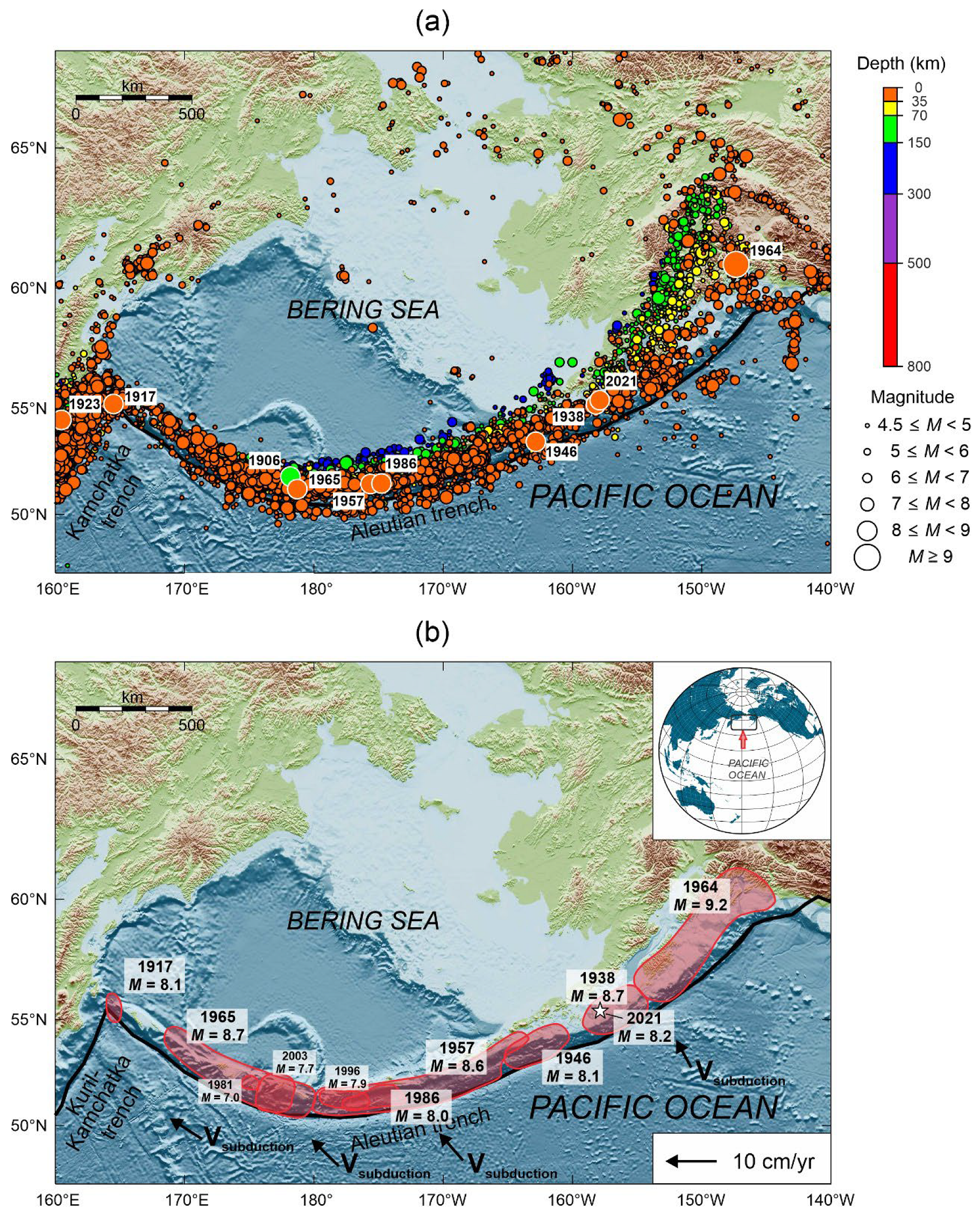
Geosciences Free Full Text Features Of The Largest Earthquake Seismic Cycles In The Western Part Of The Aleutian Subduction Zone Html
No comments for "Which Best Describes Seismic Tectonic Creep"
Post a Comment